Back Side Illumination
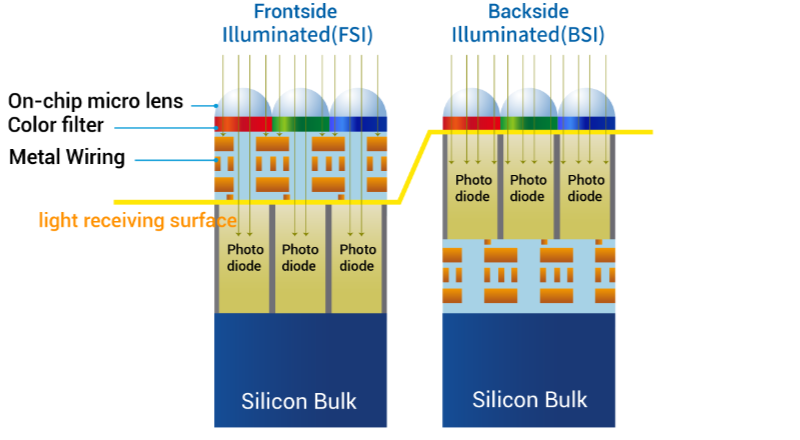
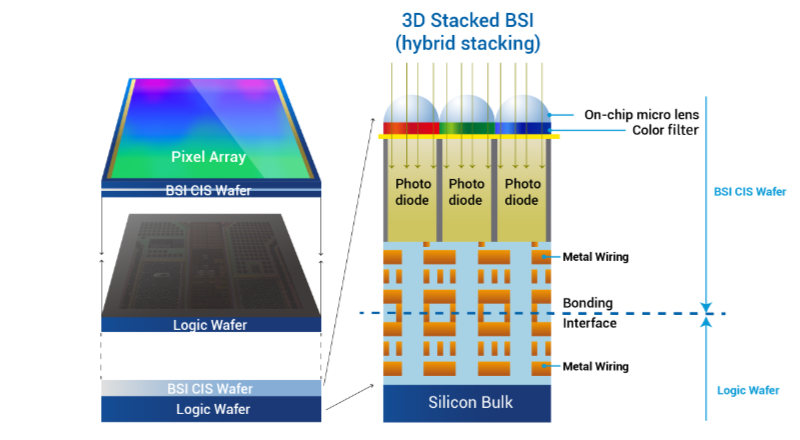
In a conventional image sensor, the photodiodes are integrated onto the silicon substrate, with the metal interconnects positioned above them. Consequently, some light gets reflected, reducing the amount of light that ultimately reaches the photosensitive layer. A back-side illuminated (BSI) sensor uses a manufacturing technique which involves flipping the silicon wafer and thinning its reverse side, allowing light to directly reach the photocathode layer without traversing through the metal wiring layer. This renders BSI sensors exceptionally well-suited for applications where superior low-light performance is essential, such as in industrial sensors, security cameras, microscope cameras, and astronomy systems. Moreover, BSI sensors offer an optimal solution for detecting non visible energy such UV light down to soft x-rays.